|
WHAT IS GRAPHENE?
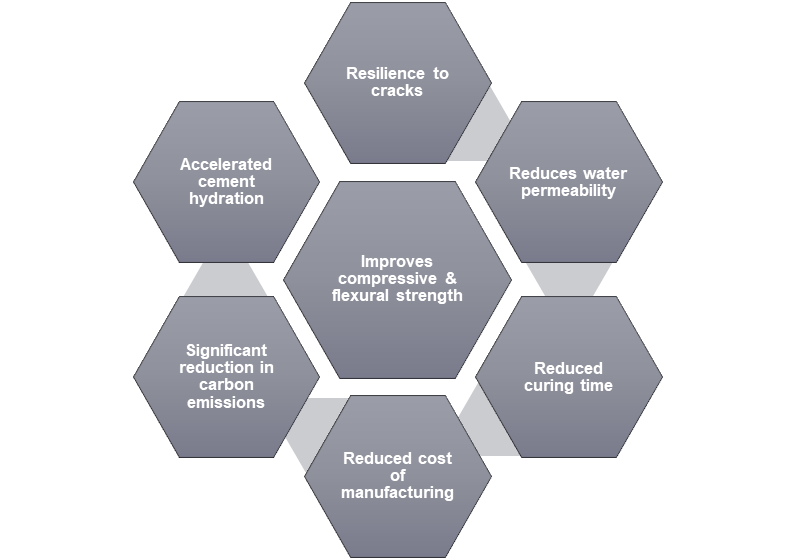
Graphene is made up of pure carbon and is commonly referred as a two-dimensional (2D) sheet-like material with carbon atoms configured in a hexagonal or honeycomb-like structure. Graphene was first isolated at The University of Manchester in 2004 by two scientists – Professor Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov – who subsequently received the Nobel Prize for Physics for their work in the field of atomically thin materials. It has been recognised as one of the most significant material discoveries of recent years because graphene’s 2D nature exhibits unique properties. It is exceedingly strong, light and flexible and is the most conductive material of both electricity and heat yet discovered. GRAPHENE IN CONCRETE By integrating graphene into concrete, engineers and architects can create structures that require less material, while still achieving the same structural performance as traditional concrete. Graphene-enhanced concrete is stronger and less water permeable than standard concrete. It uses much less cement to deliver the desired strength. As a result, it is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by 30%. When graphene is properly dispersed in concrete, it acts to fill voids and provides nucleation sites for the formation of a stronger cement microstructure upon curing. Microscope imaging of the final graphene-modified concrete materials exhibits a smaller, more evenly distributed pore network. This change in pore structure can prevent several concrete degradation mechanisms from occurring, including reduced moisture ingress, resistance to carbonation and a greater resistance to corrosive chemicals. The construction industry faces an urgent problem regarding carbon footprint, with concrete accounting for more than 7% of all global CO2 emissions. The technology improves the microstructure of concrete, significantly increasing compressive, tensile and flexural strength, reducing curing periods, microcracking and permeability. Our aim is for a 30% improvement in concrete performance, dependent on application, and proportionally decreased embodied carbon on construction projects. The challenges are an increase in cement use and the need to decarbonize the energy for its manufacture. The ‘carbon intensity’ of global cement production, CO2 emitted per tonne, continues to rise. New environmental measures pose a robust challenge but also offer a significant opportunity to those willing to think differently about innovation in construction. Traditional solutions for cement reduction in concrete are rapidly becoming unsustainable. Cement replacements such as ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBS) and pulverized fly ash (PFA) are byproducts from thermal steel-production and coal-fired power stations, which are in terminal decline. What is 2d Hexa Graphene Additive ? 2d Hexa makes graphene-enhanced additives for concrete, engineered to enhance performance and sustainability. 2d Hexa graphene dispersion has been developed to enhance the properties of concrete, aiming at upto 30% reduction in cement content and proportionally decreased embodied carbon on construction projects. The technology incorporates graphene, an atomically thin form of carbon, which improves the microstructure of concrete, significantly increasing compressive, tensile and flexural strength, reducing curing periods, microcracking and permeability. The technology has been developed for use in existing batching plants, requiring no extra training or equipment, and can be scaled at a viable cost. Application Variants : Paver Blocks, Solid Blocks, Cement Mortar, Cement Bricks, Pre-Cast Structures and more. For more information our Applications team will find help find an optimal solution for your requirements - Contact Us |
Our Products
Graphene Oxide (GO)
Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) Additives
|